
If proper separation is maintained between the crystal and its tank circuits from other components and traces on the PCB, and the loop areas are kept small, there should be no problems with this noise source. Also, any noise caused by internal operations, such as the clock buffers, appears on the output. In addition to the fundamental frequency, harmonics are introduced on the output side because the output buffer is digital, which squares the sine wave. The third noise source is the oscillator circuit, where the oscillator swings rail to rail.
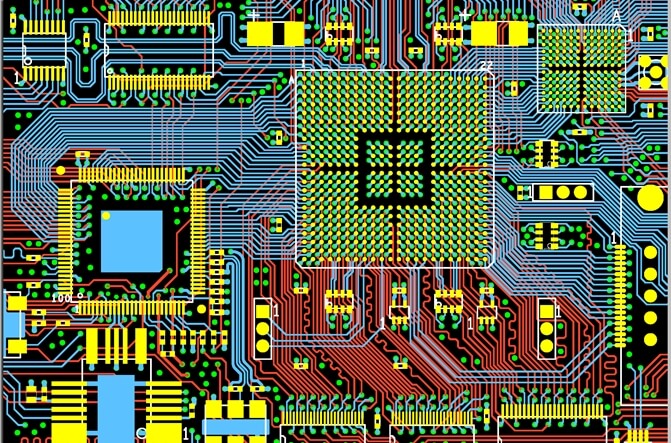
These circuits are the source of all the RF energy in the system, as they feed the clocked circuits inside the IC with the current required for switching. The second most-important contributor is the power-supply system, which includes the voltage regulation and the bypassing capacitors at both the regulator and at the microcomputer.
The synchronous nature of most devices causes all current- switching events to occur at the same time, making a large noise spike containing RF energy. The glitch is caused by the common impedance of the output pin and the clock drivers, that is, the shared pins that supply each power and ground. The noise from clock switching within the IC appears as ‘‘glitches” on a static output. These pins also connect to both internal and external cables. Because the area covered by traces connected to them on the PCB form a large antenna. The biggest problem is noise from the integrated-circuit (IC) input/output (I/O) pins. Potentially, every pin on the microcomputer can be a problem. The noise is present on all outputs, inputs, power supply, and ground at all times. This noise is generated inside the device and is coupled out in many different possible ways. Over time, as IC devices increase in speed and density, every method to isolate and reduce noise will be required.ĭesign guidelines to be discussed concern radio-frequency (RF) noise from the microcomputer. The reader is cautioned against making the assumption that although on a prior design a given technique was not applied and the unit had acceptable performance, that the technique is not useful.

This document does not always explain the why’s of a given technique because it is intended only as a reference document, not a teaching aid. This level seems to be the upper limit of acceptable noise in European and U.S. Efforts have been made to target two-layer boards, and the maximum acceptable noise level is assumed to be 30 dB, or greater, more stringent than FCC Part 15. This document covers most known and published layout techniques as applied in a low-noise, unshielded environment. Some guidelines apply specifically to microcontrollers however, the guidelines are intended to be general, and apply to virtually all modern CMOS integrated circuits. General layout guidelines for printed circuit boards (PCB), which exist in relatively obscure documents, are summarized.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
